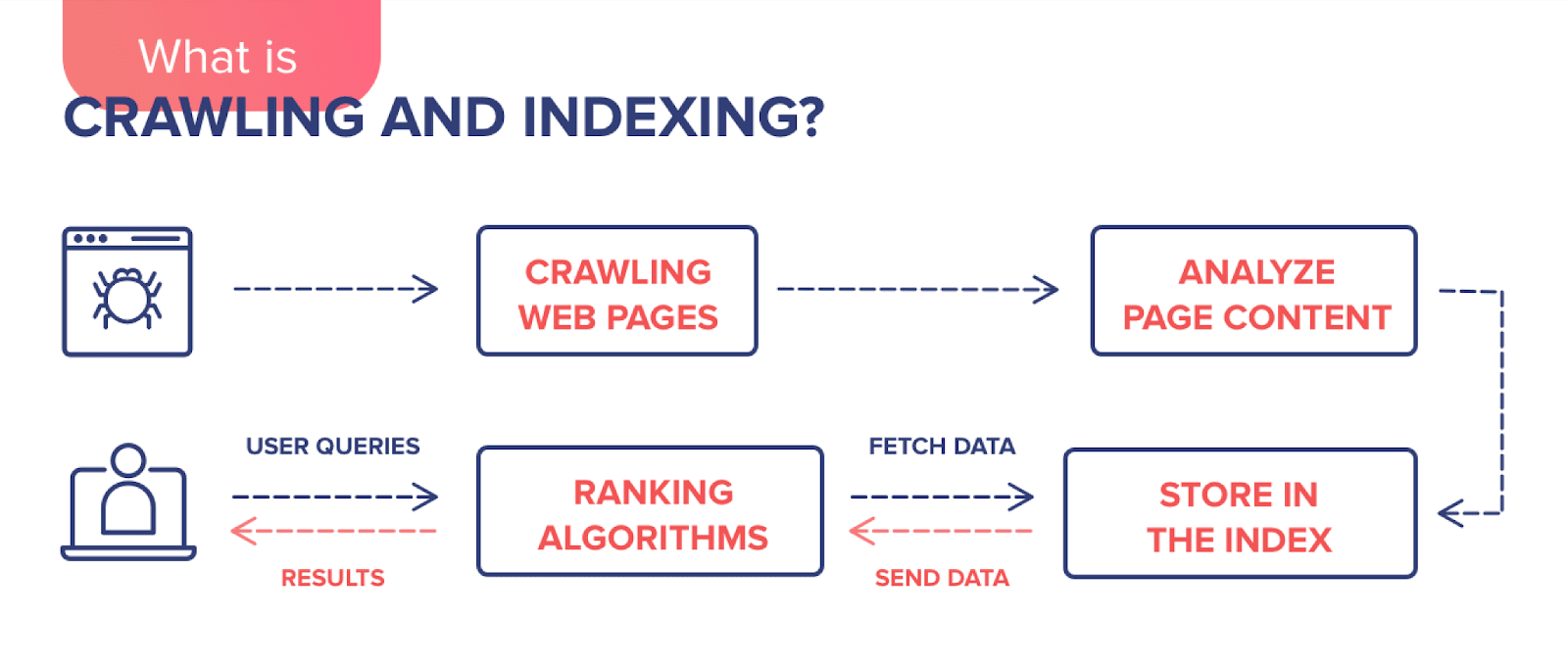
Search engine indexing – what is it?
In simple terms, the indexing of the site is the introduction of its pages in the database of search engines. During this process, the system collects information about the content of the resource. Search engine robots (they are also called spiders) scan and process web pages, videos, images, etc. Once the analysis is complete, the pages are stored in a search index – that is, a database. And it is in this database that the system then searches for results that match user queries.
How is the indexing of the site by search engines
One query is thousands of addresses that potentially contain an answer. In fact, Google knows it before the user has entered a query into the search box. Indexing is an ongoing process because web crawlers regularly scan new and updated sites, adding the information they receive to the index (database). It turns out that when a user searches for something on the Internet, he is actually looking for an index.
Subpages of the site, that is, children, coming after the main, are indexed one by one. After entering a query, the robot searches the index and finds all the relevant pages. Thus, we get a really great number of results.
To give the user the most accurate answer, Google uses algorithms that select sites in the index based on several hundred different factors. They take into account not only the number and placement of keywords and relevant word combinations, but also the quality, the usability of the site, and how well it protects sensitive data. There are a lot of ranking factors and it is necessary to correspond to each of them. In this case, the process of determining the position of the site and the display of search results from Google takes about half a second.
How many www-addresses are in the index? Hundreds of billions. They take up over 100,000,000 gigabytes. Google assigns a site to an index according to the words it contains.
Loading, indexing and algorithm performance
To determine the site that best responds to user queries, search algorithms have to work. It is through them that the results in the index are selected and arranged in a certain order. Google is constantly working to improve its algorithms, so it can recognize keywords, context, and even typos that may appear as you type. However, the algorithms assess not only text, but also other aspects such as site credibility, credibility and informative content, link quality, and even user intent.
Indexing and scanning
What page indexing is, we’ve covered. However, you may also find the term “crawling” in the context of search engines. Crawling does not yet index pages, but only moves the robot between them.
Crawling is sending the bot to the site being analyzed, whereas indexing is downloading, processing, and collecting data to include it in the search engine’s index. Crawling does not mean that the address has been indexed and will appear in search results.
Placing a web address in the index is the next step after the scan. Not every page that is scanned is indexed, but every page that is indexed has been scanned before.
Crawling crawling budget
A crawling budget is the maximum amount of data a search engine can retrieve from a domain per robot visit. To get the most out of robot crawling, there are two aspects to consider:
- Limiting the crawl speed;
- Speeding up the indexing of the site.
Robots want to scan as many URLs as possible during one visit. Limiting the crawling speed is so that they make the rounds without overloading the server. If the crawler loads too many pages, the site will start to load more slowly, and this in turn will frustrate its visitor.
Previously, this restriction required specifying the crawl-delay directive in the robots.txt file. Today, it is considered obsolete, as search engines themselves control the speed. If the server load is too high, crawling stops automatically, so “heavy” pages must be optimized to reduce their weight, and less time will be spent on their processing by robots.
To speed up the indexing, the bot forcibly returned to the site. For this new or updated pages are sent to rescan through the webmaster panel. It is worth noting that popular and frequently updated sites are processed more often, as changes on them attract the attention of search engine robots. That is why the cessation of optimization work becomes the reason for lower positions in the search engine.
In brief, the site indexing budget – the number of URLs that the search engine can and wants to index. It is expressed in megabytes (MB).
Each domain is allocated a daily budget. Bots crawl the pages to the limit and stop indexing when it is used up. Then they come back to check for updates on already loaded addresses. If the site architecture is poorly designed, pages that are too deep may not be indexed at all. To avoid this, you need to focus not so much on the beautiful design as on the usability, taking into account further optimization. Important sub-pages should be among the first in the hierarchy of the site, the rest are ordered with decreasing priority.
When the search robot returns to the site, no one knows. In theory, the scanning is carried out every day, but nowhere specified when the bot stops it, and at what time resumes.
Cyclic indexing
Indexing is cyclic, so you need to constantly worry about the quality of the site and updates are made to occupy high positions in search results. After the first visit, the robots come back from time to time to check and index any changes. The more often they encounter new, valuable content, the more likely they are to come back again. And as a bottom line: the earlier it is indexed, the faster it will appear in search results.
Fast indexing of pages in Google: how long does it take?
Why is one address crawled faster than another?
As is usually the case with Google, when it comes to indexing, the company’s experts don’t explain anything directly. In 2018, Google’s John Mueller confirmed that URLs are retained according to different factors, and that the search engine does not crawl URLs at the same frequency all the time. Therefore, it is not surprising that some sites will be visited by robots every day, others every week, others every few months or even every six months.
It is worth emphasizing that a rare site scan does not mean that there is something wrong with it from a technical point of view. Processing period of several months is quite normal and natural. As an example, we should add that making significant changes to the site will lead to the fact that some pages are indexed quickly. The rest will have to wait for a while. Why does this happen? This is influenced by many factors: the linking, the structure of the page, the frequency of changes. For example, if the site has not been updated for a long time, the search engine may not send it to the bot. However, when updates occur, it may take some time, but eventually Google’s bot will visit the changed page.
How quickly can a search engine index a page?
In most cases it takes a few days. It can take up to 24 hours, although you can’t say that it happens all the time. Webmasters admit that this is not the case: the page may appear in the index on the same day, a week, or even a month.
How long does it take to index changes to pages?
There is no simple answer to this question. Google works at a certain pace, but it is known that in addition to the frequency of updates, it also takes into account other factors. For the search robot to visit the site more often, it needs to be updated regularly. After changes are made, such as deleting or adding pages, submit a request for re-blogging through your webmaster panel. You can also leave links to new content in social networks, blogs, thematic forums.
From indexing to ranking
Without indexing you can’t get high positions in search results, because it’s a necessary step to get your site indexed by Google. Indexing itself sometimes takes several months. Once a site is saved in Google’s cache, it takes time to evaluate the changes. At this point, the page is already at some level in the rankings. You make changes to improve the rankings, and the cycle begins again.
Author of the article: Jeff Vertes (online casino and SEO expert)